Please fill in some of the data provided below to receive the latest Toyota-related news and information in your email.
Since its early presence, Toyota has a vision of developing the Indonesian automotive industry. As proof, Toyota's initial steps were accompanied by the establishment of a factory that has continued to grow until now, as well as serving as the vanguard of product localization.
Although the manufacturing sector is believed to be a hanger for economic progress, not many countries in the world have succeeded in realizing the dream of modernity. The scarcity of experts, the undeveloped research and technology, until the fulfillment of economies of scale is an obstacle for anyone paving the way for the industry.
On the other hand, in the industrial arena, corporate giants always treat these three forces as a secret heirloom. Many are reluctant to share with outsiders.
On the contrary, it is common for industrial development for a country to be marked by hatching factories. Through the factory, the mass production process until technology transfer occurs.
So, no exaggeration of Toyota's action coupled with investment in building a factory is a commitment to support the advancement of the industry in Indonesia. The official operation of Toyota Indonesia began in 1971, although a decade before Toyota's product range was familiar with consumers in the country.
It only took two years after the establishment of PT Toyota Astra Motor (now PT Toyota Motor Manufacturing Indonesia and PT Toyota Astra Motor), Toyota Indonesia has established an assembly plant facility. This plant was made by PT Multi Astra as an assembly plant in 1973, following the operation of the PT Toyota Mobilindo car body manufacturing plant as a vehicle body manufacturer in 1977, and was equipped with Toyota Engine Indonesia as an engine manufacturing plant in 1982.
Seeing this persistence, Toyota can be said to be serious about encouraging Indonesia to obtain a production base status. The establishment of Toyota Mobilindo marks a new round of the national automotive world because one of the main parts of the body has been worked on by local factories.
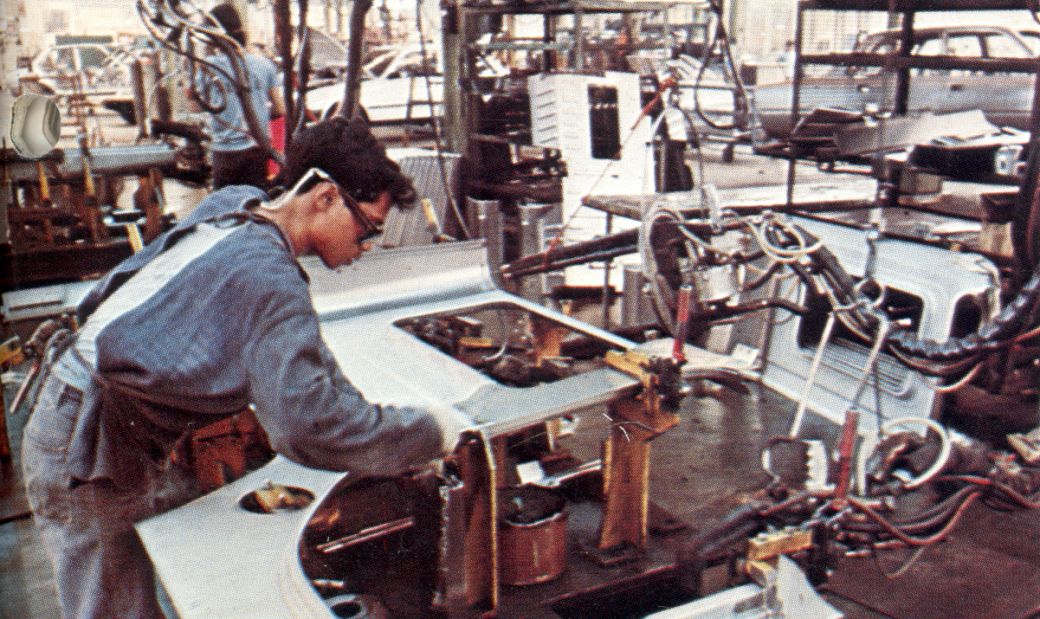
The presence of Toyota Mobilindo which occupies the factory area in Sunter, North Jakarta, firstly introduced heavy technology in automotive production to the public. A total of 12 press machines were shipped directly from Japan.
The machines have the same technology used in Japan with various functions, there are uses in the process of bending plates and iron, to making chassis. During the initial process, Toyota Indonesia has sent local workers to directly study at the Toyota Toyota factory center.
During this initial stage, the Toyota Mobilindo factory focused on producing the phenomenal needs of the Kijang, and Hi Ace products. In turn, only a year later, Toyota Mobilindo built a new factory complex that became known as the Sunter II factory.
Following the production of Hi Ace, Toyota Mobilindo also directly brought production equipment from Japan. Until entering the 1980s, the Toyota-owned factory received additional product focus namely the Toyota Dyna.
The production of several key components of the Kijang, Hi Ace, and Toyota Dyna remains with Toyota Moblindo. To fulfill the increasing orders from year to year, Toyota Mobilindo began to add its production machines.
In turn, Toyota Mobilindo no longer needs to ship press machines from Japan. Through the presence of the Toyota Indonesia factory, local partners emerged who were successfully encouraged to produce similar machines of equal quality.
Industry, Industri OtomotifMedia/Journalist Contact : [Memuat email...]
Non Media / Non Journalist Contact : [Memuat email...]
© 2024 Toyota Motor Manufacturing Indonesia. All Rights Reserved.
