Please fill in some of the data provided below to receive the latest Toyota-related news and information in your email.

Europe once faced a disaster resulting from technological advancement. Yes, when many people celebrated “Industrial Revolution” taking place in the 18th and 19th centuries, numerous social and economic problems also emerged.
At that time, the technological progress in textile manufacturing, enabled by the invention of various machines, followed by the invention of the steam engine, supported mechanical production. The Industrial Revolution, whose epicenter was the Great Britain, replaced the use of animal and human power with machines.
Efficient production happened rapidly. Apart from the decline in production costs thanks to the utilization of machines, the transportation became more efficient with the presence of locomotives and steam-powered vessels.
But, immediately the condition triggered by the industrial revolution caused numerous social and economic problems. Amid the surplus of production, the market dimmed following the fall of labor wage because of over-employment. Europe gradually entered a crisis. Various social unrests hit “the Blue Continent”. There was no measure taken in anticipation of technological advancement.
on the other hand, the world is now grappling with the Fourth Industrial Revolution (IR 4.0). The information technological progress impacts all aspects of life.
The present era seems to justify the adage of economist Thomas Friedman that the world is flat. Globalization has been increasingly amplified by the advancement of the information technology marked by the use of Internet of Things (IoT).
With the power of computerization and Internet connection, the digitalization also changes the way of life in the society, business processes and manufacturing. Conventional and inadaptive things are exposed to disruption.
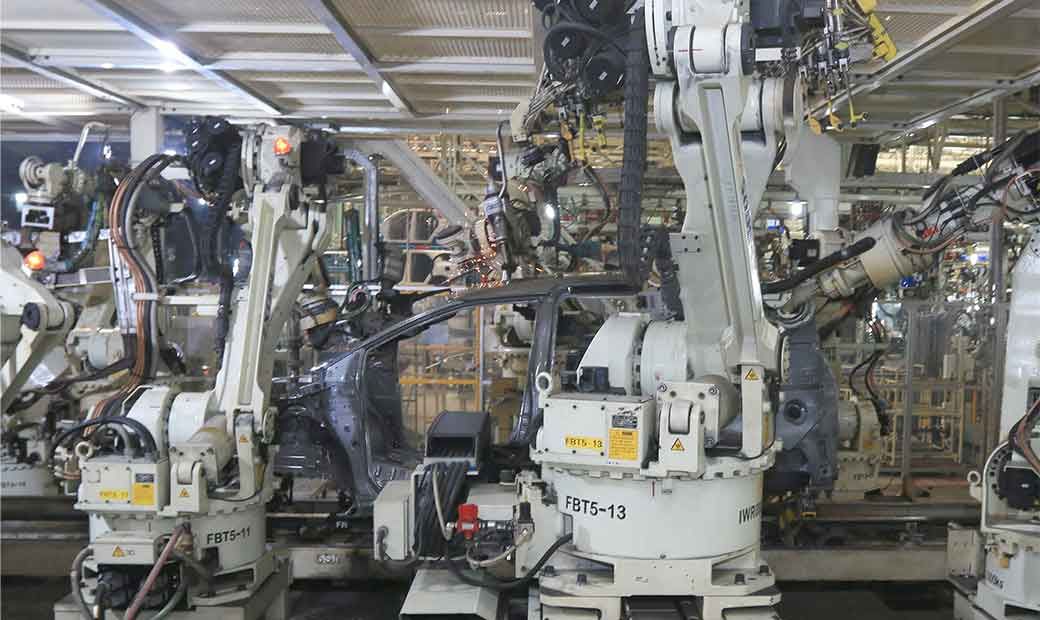
The similar wave also hit the automotive sector. Amid the wave of the IR 4.0, automotive manufacturers have developed a lot of things, from the production side to the application of digital technology in products.
The automation technology, which changes the production method, promises efficiency for manufacturers. The use of robots in production to multiply volume and cut production time becomes a norm.
On the similar wave, the automotive sector succeeds to direct the digital technology toward driving automation, a driverless car. Another latest technology is the development of environmentally-friendly products, such as electric motorized vehicles.
At the global stage, each manufacturer enters the race to design the sophisticated products. This results in a tighter competition amongst manufacturers and producing countries.
Reading these signs, the Indonesian government is agile to prepare for the fundamentals for the domestic automotive industry. As a priority manufacturing sector, the automotive industry is expected to ride on the wave of IR 4.0.
The automotive sector is included in the development objectives of the Making Indonesia 4.0 roadmap. It is expected that the sector can make Indonesia the qualified production base that adopts sophisticated technology.
Furthermore, the government encourages that producers pioneers the production of electric motorized vehicles (KBL) in accordance with the global automotive development trend. With two crucial points – the use of the IR 4.0 technology and the development of electric motorized vehicles – the government expects to boost automotive export.
In the past few years, the export of the completely-built up vehicles had hit 300,000 units, up significantly from the last five years. This was quite encouraging as the domestic market stagnated.
Drawing a lesson from the past industrial revolution, the desire to catch up with IR 4.0 technological progress must be supplemented by the maturity of manufacturing and anticipative measures. The automotive sector is one of the labor-intensive industrial sectors due to its long supply chain.
Human Resources at the Center of Transformation
The Indonesian automotive industry has a long history, and Toyota is no exception. The development of manufacturing from the construction of plants to local suppliers has been successfully carried out.
Furthermore, as the indication of the application of high technology, manufacturers have conducted computerized research and development (RnD) and production processes and make best use of Internet connection. Actually, the utilization of the advanced technology seeks to support the reliability of the flawless production system and guarantee the excellent product quality without setting aside the safety of workers.
For Toyota, the implementation of IR 4.0 does not mean reducing labor absorption and replacing manpower with robotic technology. The capacity building of human resources who are technologically “literate” at the center of transformation is key to the success of the IR 4.0 implementation.
Toyota believes that the IR 4.0 serves as a means to achieve greater efficiency and productivity.
The man behind the gun remains the target of quality improvement conducted by Toyota Indonesia. A similar spirit is transmitted to many parties, especially those engaging in its supply chain.
Some new features applied in the development of Toyota’s human resources to address the challenges of IR 4.0 implementation are artificial intelligence, connectivity and cloud computing.
IR4.0, SDM, People Development, Revolusi IndustriMedia/Journalist Contact : [Memuat email...]
Non Media / Non Journalist Contact : [Memuat email...]
© 2024 Toyota Motor Manufacturing Indonesia. All Rights Reserved.
