Please fill in some of the data provided below to receive the latest Toyota-related news and information in your email.
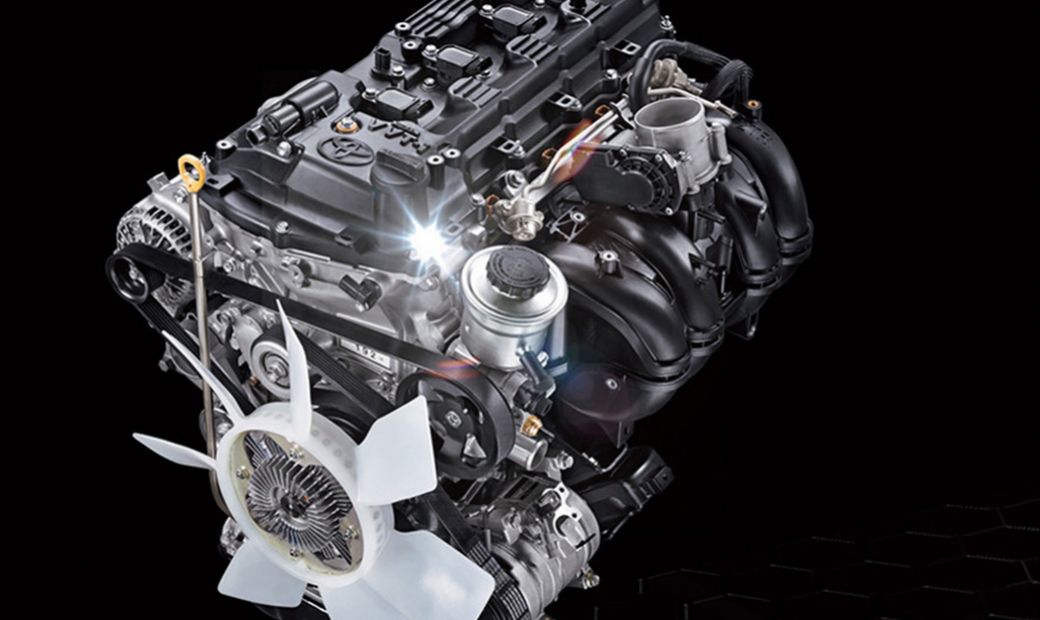

Seeking for engine power is generally compensation for fuel usage. But thanks to the variable valve technology developed by Toyota, VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing with Intelligence), these two characters can compromise with each other. Car engines can produce more maximum power, but still fuel-efficient. How did this happen? Let's look at the internal parts of this 4-stroke gasoline runway kitchen.
In conventional internal combustion engines, the introduction of a mixture of fuel and air is controlled by a valve in the inlet. Including the combustion of residual combustion gas, regulated exhaust valve into the exhaust. Combustion in the engine will be greatly influenced by various driving conditions. For example, driving casually in the city, or racing at high speed on the freeway.
Both conditions require different combustion in the engine. In relaxed driving conditions, only a little mixture of fuel and air is needed. But after developing speed, the engine will spin faster, so it needs a mixture of fuel and more air.
From that condition, variable valve technology was developed. Toyota introduced this technology as the VVT (Variable Valve Timing) in 1991 in a 4A-FE engine with a configuration of 5 valves per cylinder. Then in 1995, new VVT-i technology was introduced in 1JZ-GTE and 2JZ-GTE engines.
MECHANISM
Broadly speaking, the VVT-i system is in the cylinder head area to control the valve opening time. In this system, the opening valve is set. From the results of the study, opening the valve earlier and closing it faster will provide better power at low engine speeds.
For example, in general, during a suction step on a 4-stroke engine, the inlet valve will start to open at 5 degrees before the Upper Dead Point (TDC) of the piston and close at 185 degrees after the TDC. So, opening the inlet valve at 15 degrees before TDC and closing it at 175 degrees after TDC will provide more prime power with the same fuel and air alloys.
Vice versa, opening the inlet 5 degrees after TDC and closing it 195 degrees after TDC will give a better power effect at high engine speed. The effect, better combustion, fuel consumption remains minimal but power rises.
Shifting the valve opening time can be done by adjusting the camshaft movement. In the VVT-i system, this is done using a hydraulic device found on the gear that rotates the camshaft. Inside this camshaft gear, there is oil-filled space, which shifts the camshaft's movement, rotates faster or slower.
DUAL VVT-i
Not only the inlet valve can be maximized. The exhaust valve can be controlled to get better results. This system was first introduced at the Toyota Altezza RS200 with a 3S-GE engine in 1998. This system is present today and provides excellent efficiency and power and good emissions.
VVTL-i
In addition to controlling valve opening time, Toyota is also developing a high-tech variable valve opening. So that two variations of aperture (timing) and height (lift) can be obtained on the VVTL-i system (Variable Valve Timing and Lift with Intelligence). The mechanism is different in the valve trigger part. At low engine speed, the trigger will move the valve. But once the engine speed rises, there is a kind of pin inside the valve trigger that will shift so that it adds to the valve opening. The effect, at a high rotation of the fuel mixture and more air into the combustion chamber. This system was first introduced in 1999 for the Toyota Celica with a 2,000cc 4-cylinder inline 2ZZ-GE engine.
VALVEMATIC
Increasingly sophisticated, valve openings can now be controlled to replace the function of the gas skep. Valvematic can continuously control the valve opening time and height. Thus, it can regulate the intake of a mixture of fuel and air. So, this system also replaces the function of the throttle valve or gas receptor. This technology first appeared in 2007 and is present in Indonesia on the Toyota NAV-1.
Valve, VVT-iMedia/Journalist Contact : tmmin.pr@toyota.co.id
Non Media / Non Journalist Contact : admin.website@toyota.co.id
© 2024 Toyota Motor Manufacturing Indonesia. All Rights Reserved.
